반응형
ubuntu에서 libdasm라이브러리 사용해서 disassembly 보기
1. 라이브러리 컴파일
wget https://storage.googleapis.com/google-code-archive-downloads/v2/code.google.com/libdasm/libdasm-1.5.tar.gz tar xvfz libdasm-1.5.tar.gz cd libdasm-1.5 make sudo make install
2.makefile
# # Makefile for example programs # Requires libdasm static lib (libdasm.a) # CC = gcc CFLAGS = -Wall -O3 das: das.o $(CC) $(CFLAGS) -o das das.o ../libdasm.a clean: rm -f das *.o
3.소스
/*
* das.c -- simple 32-bit example disassembler program
* (c) 2004 - 2005 jt / nologin.org
*
* How to compile in MSVC environment:
* cl das.c ../libdasm.c
*
* In Unix environment, use the supplied Makefile
*
*/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <signal.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include "../libdasm.h" // include libdasm.h
#define MIN(x, y) ((x) < (y) ? (x) : (y))
unsigned char * read_file(int *, char *);
/*
* Handler for segmentation faults
* If this fires, there's probably bug in libdasm parsing code
*
*/
void sighandler(int sig) {
printf("*** SIGSEGV catched\n");
exit (1);
}
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
INSTRUCTION inst; // declare struct INSTRUCTION
unsigned char *data;
int i, c = 0, bytes, format = FORMAT_INTEL, size, len;
char string[256];
if (argc < 2) {
printf("\nLibdasm example, compiled with version %d.%d.%d.%d\n\n",
GET_VERSION_MAJOR,
GET_VERSION_MINOR1,
GET_VERSION_MINOR2,
GET_VERSION_MINOR3);
printf("Usage: %s <file> [-a|-i] [bytes]\n"
" file file to be disassembled (required)\n"
" -a format: ATT (optional)\n"
" -i format: INTEL (optional, default)\n"
" bytes show raw instruction data (optional, default 8)\n\n",
argv[0]);
exit (1);
}
data = read_file(&size, argv[1]);
bytes = 8;
if (argc > 2) {
if (argv[2][0] == '-') {
switch(argv[2][1]) {
case 'a':
format = FORMAT_ATT;
break;
case 'i':
format = FORMAT_INTEL;
break;
}
if (argc > 3)
bytes = atoi(argv[3]);
} else
bytes = atoi(argv[2]);
}
signal(SIGSEGV, sighandler);
while (c < size) {
/*
* get_instruction() has the following parameters:
*
* - &inst is a pointer to struct INSTRUCTION
* - data + c is pointer to data to be disassembled
* - disassemble in 32-bit mode: MODE_32
*/
len = get_instruction(&inst, data + c, MODE_32);
// Illegal opcode or opcode longer than remaining buffer
if (!len || (len + c > size)) {
printf("%.8x ", c);
if (bytes) {
printf("%.2x ", data[c]);
for (i = 1; i < bytes*2 - 1; i++)
printf(" ");
}
if (format == FORMAT_INTEL)
printf("db 0x%.2x\n", *(data + c));
else
printf(".byte 0x%.2x\n", *(data + c));
c++;
continue;
}
/*
* Print absolute offset and raw data bytes up to 'bytes'
* (not needed, but looks nice).
*
*/
printf("%.8x ", c);
if (bytes) {
for (i = 0; i < MIN(bytes, len); i++)
printf("%.2x", data[c + i]);
printf(" ");
for (i = MIN(bytes, len); i < bytes*2 - len; i++)
printf(" ");
}
/*
* Print the parsed instruction, format using user-supplied
* format. We could of course format the instruction in some
* other way by accessing struct INSTRUCTION members directly.
*/
get_instruction_string(&inst, format, (DWORD)c, string, sizeof(string));
printf("%s\n", string);
c += len;
}
return 0;
}
/* Read file in buffer */
unsigned char * read_file(int *len, char *name) {
char *buf;
FILE *fp;
int c;
struct stat sstat;
if ((fp = fopen(name, "r+b")) == NULL) {
fprintf(stderr,"Error: unable to open file \"%s\"\n", name);
exit(0);
}
/* Get file len */
if ((c = stat(name, &sstat)) == -1) {
fprintf(stderr,"Error: stat\n");
exit (1);
}
*len = sstat.st_size;
/* Allocate space for file */
if (!(buf = (char *)malloc(*len))) {
fprintf(stderr,"Error: malloc\n");
exit (1);
}
/* Read file in allocated space */
if ((c = fread(buf, 1, *len, fp)) != *len) {
fprintf(stderr,"Error: fread\n");
exit (1);
}
fclose(fp);
return (buf);
}
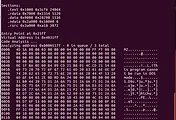
결과
반응형
'debug > 0x09-gdb' 카테고리의 다른 글
| pyew 간단한 사용법 (0) | 2016.12.15 |
|---|